Semiconductor and Consumer Electronics Dynamics: iPhone 17 Memory Differentiation, Cadence Launches LPDDR6 IP
iPhone 17 Series Memory Configuration Differentiation, Entry - level Models Adopting LPDDR5 Draws Attention
The memory configuration of Apple’s upcoming iPhone 17 series has sparked industry discussions, with a clear differentiation between entry – level and high – end models. It is reported that the entry – level iPhone 17 and iPhone 17 Air will adopt LPDDR5 RAM, while the iPhone 17 Pro and Pro Max will be upgraded to 12GB LPDDR5X.
Specifically, the entry – level iPhone 17 is equipped with 8GB LPDDR5. Although the iPhone 17 Air increases the memory capacity to 12GB, it also uses LPDDR5. The Pro series, on the other hand, is equipped with 12GB of LPDDR5X. It is worth noting that compared with LPDDR5, LPDDR5X has higher bandwidth and better energy efficiency. In bandwidth – intensive scenarios, it can enable faster application startup, smoother multitasking, and longer battery life. However, the entry – level iPhone 17 is rumored to have a battery capacity of only 2800mAh, and the memory downgrade has caused controversy in terms of performance and energy efficiency.

Industry analysis suggests that the iPhone 17 Air is positioned as a slim and low – cost alternative to the Pro models. The adoption of LPDDR5 may aim to reduce production costs, better match the low – power SoC version, and at the same time keep the device running at a low temperature and efficiently under moderate loads. Ironically, though, LPDDR5X is more efficient under sustained loads. Apple expects that ordinary users will hardly notice a significant difference in daily use, and users sensitive to performance may be more inclined to choose the Pro series. The iPhone 17 series is scheduled to be officially launched in September this year.
Cadence Launches Industry's First LPDDR6 Memory IP to Accelerate AI Computing Power Support
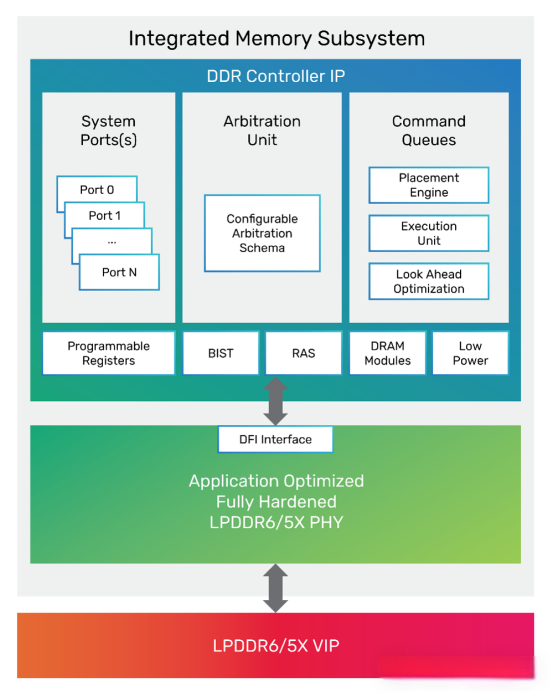
Semiconductor design solutions provider Cadence recently announced that the industry’s first LPDDR6/5X memory IP system solution has completed tape – out. This solution operates at a speed of up to 14.4Gbps, which is 50% higher than the previous generation of LPDDR DRAM, and will provide key support for the fields of AI, high – performance computing (HPC), and data centers.
It is reported that Cadence’s LPDDR6/5X IP meets the JEDEC standard. It integrates an advanced PHY architecture and a high – performance controller, optimizing power consumption, performance, and area (PPA). At the same time, it supports LPDDR6 and LPDDR5X dual protocols, providing higher flexibility. Relying on the Cadence Chiplet framework, this solution can be natively integrated into traditional monolithic SoCs and multi – chip system architectures, facilitating heterogeneous Chiplet integration. Its UCIe – based chip framework was verified in tape – out in 2024.
With the rise of AI technology, the increasing complexity of algorithms has made the demand for data and computing power exceed the capacity of existing infrastructure. Cadence’s new LPDDR6/5X 14.4Gbps memory IP not only represents a technological upgrade but also serves as a fundamental enabler for expanding AI workloads, from large language models (LLMs) to real – time agent systems. By addressing key bottlenecks in memory bandwidth and power consumption, it is positioned to gain a premium in the semiconductor market driven by AI – driven demand.
In terms of market prospects, it is expected that the artificial intelligence data center market will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 27.1% to 157.3 billion US dollars by 2034, and the LPDDR5X segment market will expand at a compound annual growth rate of 28%. Currently, Cadence has carried out multiple cooperations with leading AI, HPC, and data center customers. Its 14.4Gbps IP has become a key configuration for the next – generation AI chip design and is expected to take the first – mover advantage in the 50 billion US dollar AI chip market and the future 45 billion US dollar expenditure on AI cloud infrastructure, further consolidating its moat in the memory IP field.
